Molecular degree of perturbation of plasma inflammatory markers associated with tuberculosis reveals distinct disease profiles between Indian and Chinese populations.
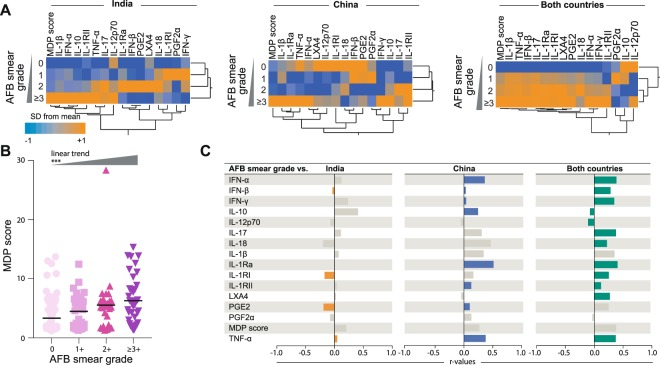
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic inflammatory disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection which causes tremendous morbidity and mortality worldwide. Clinical presentation of TB patients is very diverse and disease heterogeneity is associated with changes in biomarker signatures. Here, we compared at the molecular level the extent of individual inflammatory perturbation of plasma protein and lipid mediators associated with TB in patients in China versus India. We performed a cross-sectional study analyzing the overall degree of inflammatory perturbation in treatment-naïve pulmonary TB patients and uninfected individuals from India (TB: n = 97, healthy: n = 20) and China (TB: n = 100, healthy: n = 11). We employed the molecular degree of perturbation (MDP) adapted to plasma biomarkers to examine the overall changes in inflammation between these countries. M. tuberculosis infection caused a significant degree of molecular perturbation in patients from both countries, with higher perturbation detected in India. Interestingly, there were differences in biomarker perturbation patterns and the overall degree of inflammation. Patients with severe TB exhibited increased MDP values and Indian patients with this condition exhibited even higher degree of perturbation compared to Chinese patients. Network analyses identified IFN-α, IFN-β, IL-1RI and TNF-α as combined biomarkers that account for the overall molecular perturbation in the entire study population. Our results delineate the magnitude of the systemic inflammatory perturbation in pulmonary TB and reveal qualitative changes in inflammatory profiles between two countries with high disease prevalence.
Authors
Deivide Oliveira-de-Souza; Caian L Vinhaes; Maria B Arriaga; Nathella Pavan Kumar; Juan M Cubillos-Angulo; Ruiru Shi; Wang Wei; Xing Yuan; Guolong Zhang; Ying Cai; Clifton E Barry; Laura E Via; Alan Sher; Subash Babu; Katrin D Mayer-Barber; Helder I Nakaya; Kiyoshi F Fukutani; Bruno B Andrade
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Microbiology or Immunology
Lista de serviços
-
Genomic analyses reveal broad impact of miR-137 on genes associated with malignant transformation and neuronal differentiation in glioblastoma cells.Genomic analyses reveal broad impact of miR-137 on genes associated with malignant transformation and neuronal differentiation in glioblastoma cells.
-
RNA-Binding Protein Musashi1 Is a Central Regulator of Adhesion Pathways in Glioblastoma.RNA-Binding Protein Musashi1 Is a Central Regulator of Adhesion Pathways in Glioblastoma.
-
MicroRNA Transcriptome Profiling in Heart of Trypanosoma cruzi-Infected Mice: Parasitological and Cardiological Outcomes.MicroRNA Transcriptome Profiling in Heart of Trypanosoma cruzi-Infected Mice: Parasitological and Cardiological Outcomes.
-
Genome mapping and expression analyses of human intronic noncoding RNAs reveal tissue-specific patterns and enrichment in genes related to regulation of transcription.Genome mapping and expression analyses of human intronic noncoding RNAs reveal tissue-specific patterns and enrichment in genes related to regulation of transcription.
-
Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 participates in the transcriptional regulation of melanoma cells.Antimicrobial peptide LL-37 participates in the transcriptional regulation of melanoma cells.
-
Down-regulation of 14q32-encoded miRNAs and tumor suppressor role for miR-654-3p in papillary thyroid cancer.Down-regulation of 14q32-encoded miRNAs and tumor suppressor role for miR-654-3p in papillary thyroid cancer.
-
Integration of miRNA and gene expression profiles suggest a role for miRNAs in the pathobiological processes of acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection.Integration of miRNA and gene expression profiles suggest a role for miRNAs in the pathobiological processes of acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection.
-
Integrative Biology Approaches Applied to Human DiseasesIntegrative Biology Approaches Applied to Human Diseases
-
Proteomics reveals disturbances in the immune response and energy metabolism of monocytes from patients with septic shock.Proteomics reveals disturbances in the immune response and energy metabolism of monocytes from patients with septic shock.
-
Genomics, epigenomics and pharmacogenomics of Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FHBGEP): A study protocol.Genomics, epigenomics and pharmacogenomics of Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FHBGEP): A study protocol.
-
Melatonin-Index as a biomarker for predicting the distribution of presymptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriersMelatonin-Index as a biomarker for predicting the distribution of presymptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers
-
Profiling plasma-extracellular vesicle proteins and microRNAs in diabetes onset in middle-aged male participants in the ELSA-Brasil study.Profiling plasma-extracellular vesicle proteins and microRNAs in diabetes onset in middle-aged male participants in the ELSA-Brasil study.
-
Big Data and machine learning in cancer theranosticsBig Data and machine learning in cancer theranostics
-
Genomic positional conservation identifies topological anchor point RNAs linked to developmental loci.Genomic positional conservation identifies topological anchor point RNAs linked to developmental loci.
-
Integrative systems immunology uncovers molecular networks of the cell cycle that stratify COVID-19 severityIntegrative systems immunology uncovers molecular networks of the cell cycle that stratify COVID-19 severity