Discordant congenital Zika syndrome twins show differential in vitro viral susceptibility of neural progenitor cells.
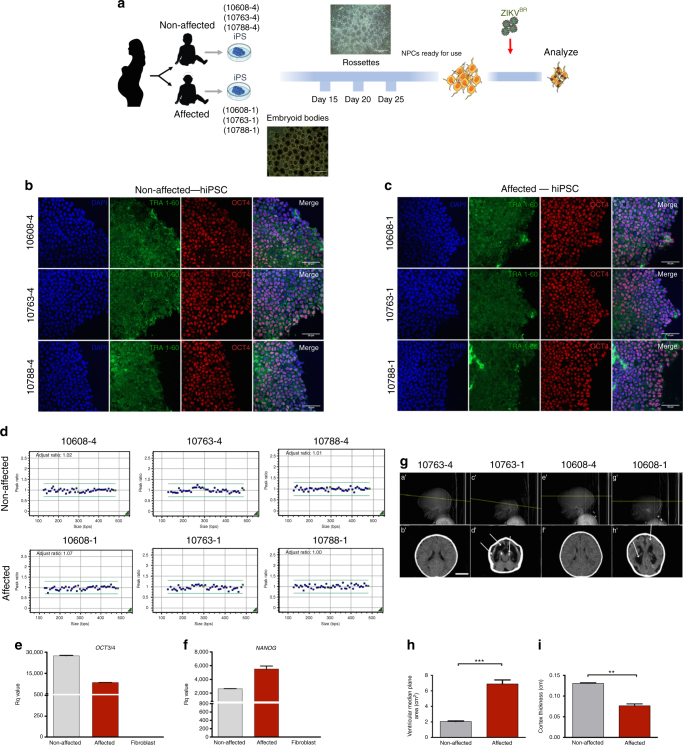
Congenital Zika syndrome (CZS) causes early brain development impairment by affecting neural progenitor cells (NPCs). Here, we analyze NPCs from three pairs of dizygotic twins discordant for CZS. We compare by RNA-Seq the NPCs derived from CZS-affected and CZS-unaffected twins. Prior to Zika virus (ZIKV) infection the NPCs from CZS babies show a significantly different gene expression signature of mTOR and Wnt pathway regulators, key to a neurodevelopmental program. Following ZIKV in vitro infection, cells from affected individuals have significantly higher ZIKV replication and reduced cell growth. Whole-exome analysis in 18 affected CZS babies as compared to 5 unaffected twins and 609 controls excludes a monogenic model to explain resistance or increased susceptibility to CZS development. Overall, our results indicate that CZS is not a stochastic event and depends on NPC intrinsic susceptibility, possibly related to oligogenic and/or epigenetic mechanisms.
Authors
Luiz Carlos Caires-Júnior; Ernesto Goulart; Uirá Souto Melo; Bruno Henrique Silva Araujo; Lucas Alvizi; Alessandra Soares-Schanoski; Danyllo Felipe de Oliveira; Gerson Shigeru Kobayashi; Karina Griesi-Oliveira; Camila Manso Musso; Murilo Sena Amaral; Lucas Ferreira daSilva; Renato Mancini Astray; Sandra Fernanda Suárez-Patiño; Daniella Cristina Ventini; Sérgio Gomes da Silva; Guilherme Lopes Yamamoto; Suzana Ezquina; Michel Satya Naslavsky; Kayque Alves Telles-Silva; Karina Weinmann; Vanessa van der Linden; Helio van der Linden; João Ricardo Mendes de Oliveira; Nivia Maria Rodrigues Arrais; Adriana Melo; Thalita Figueiredo; Silvana Santos; Joanna Goes Castro Meira; Saulo Duarte Passos; Roque Pacheco de Almeida; Ana Jovina Barreto Bispo; Esper Abrão Cavalheiro; Jorge Kalil; Edécio Cunha-Neto; Helder Nakaya; Robert Andreata-Santos; Luis Carlos de Souza Ferreira; Sergio Verjovski-Almeida; Paulo Lee Ho; Maria Rita Passos-Bueno; Mayana Zatz
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.
-
Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.
-
Network Medicine: Methods and ApplicationsNetwork Medicine: Methods and Applications
-
ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.
-
Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.
-
Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.
-
In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.
-
The evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseasesThe evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseases
-
Network vaccinology.Network vaccinology.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammationPyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammation
-
Transcriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patientsTranscriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patients
-
Gene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian BrazilGene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian Brazil
-
In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.
-
Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.
-
Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.
-
Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.