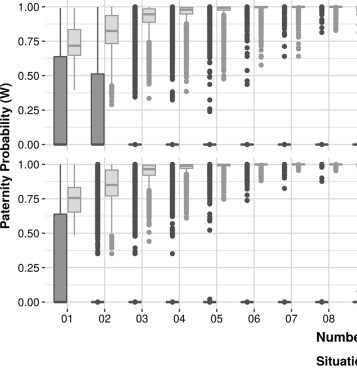
Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.
The use of noninvasive techniques to determine paternity prenatally is increasing because it reduces the risks associated with invasive procedures. Current methods, based on SNPs, use the analysis of at least 148 markers, on average. To reduce the number of regions, we used microhaplotypes, which are chromosomal segments smaller than 200 bp containing two or more SNPs. Our method employs massively parallel sequencing and analysis of microhaplotypes as genetic markers. We tested 20 microhaplotypes and ascertained that 19 obey Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and are independent, and data from the 1000 Genomes Project were used for population frequency and simulations. We performed simulations of true and false paternity, using the 1000 Genomes Project data, to confirm if the microhaplotypes could be used as genetic markers. We observed that at least 13 microhaplotypes should be used to decrease the chances of false positives. Then, we applied the method in 31 trios, and it was able to correctly assign the fatherhood in cases where the alleged father was the real father, excluding the inconclusive results. We also cross evaluated the mother-plasma duos with the alleged fathers for false inclusions within our data, and we observed that the use of at least 15 microhaplotypes in real data also decreases the false inclusions. In this work, we demonstrated that microhaplotypes can be used to determine prenatal paternity by using only 15 regions and with admixtures of DNA.
Authors
Jaqueline Yu Ting Wang; Martin R Whittle; Renato David Puga; Anatoly Yambartsev; André Fujita; Helder I Nakaya
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
User-friendly computational Tools
Lista de serviços
-
Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.
-
Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.
-
Network Medicine: Methods and ApplicationsNetwork Medicine: Methods and Applications
-
ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.
-
Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.
-
Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.
-
In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.
-
The evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseasesThe evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseases
-
Network vaccinology.Network vaccinology.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammationPyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammation
-
Transcriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patientsTranscriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patients
-
Gene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian BrazilGene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian Brazil
-
In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.
-
Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.
-
Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.
-
Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.