Replication, safety and immunogenicity of the vectored Ebola vaccine rVSV-ΔG-ZEBOV-GP in a sub-Saharan African paediatric population: A randomised controlled, open-label trial in children aged 1-12 years living in Lambaréné, Gabon.
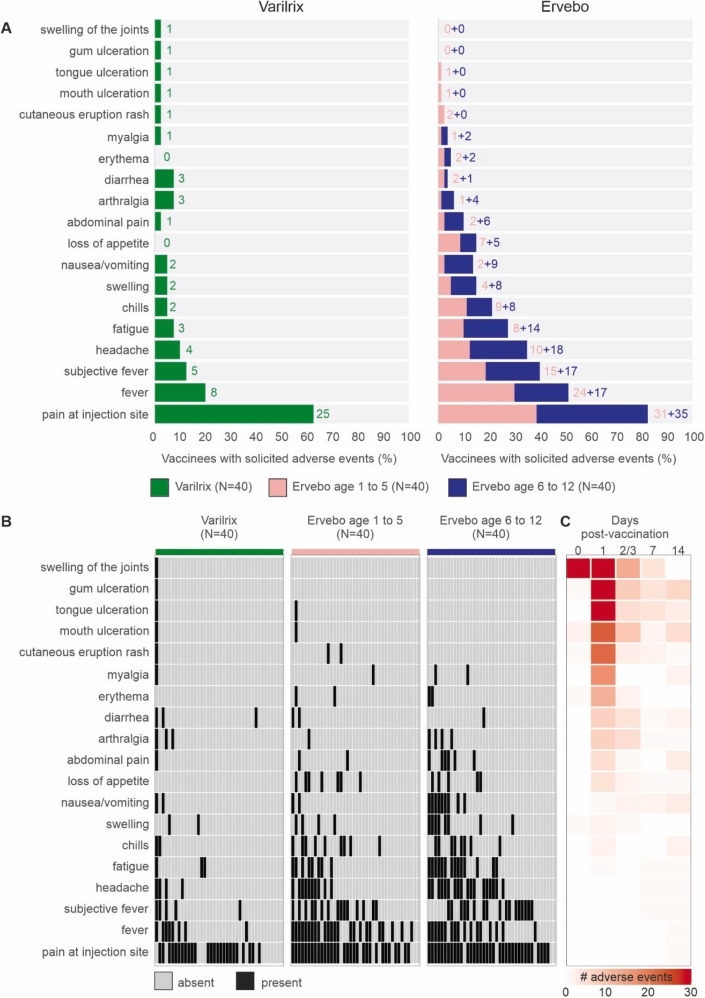
BACKGROUND: Unlike adults, children experienced stronger and longer vector replication in plasma and shedding in saliva following rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP vaccination. The resulting risks of immunosuppression or immune hyperactivation leading to increased Adverse Events (AEs) and altered antibody responses are concerns that have been addressed in the present manuscript. METHODS: Children aged 1-12 years living in Gabon received either rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP (ERVEBO®) vaccine or the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) vaccine (VZV). The concentration of rVSVΔG vector in blood and saliva, the occurrence of AEs up to day 28; the anti-rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP and anti-VZV IgG antibody titres, neutralising and avidity functions of anti-rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP by day 365; were assessed in serum. (PACTR202005733552021) FINDINGS: In the rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP group, 70% and 7% of children had >0 copies/ml of rVSVΔG respectively in plasma by day 3 and in saliva by day 14 after vaccination, with no detection on day 28. Significantly higher but transient AEs occurred in the rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP group. Both vaccines induced seroconversion on day 28 and sustainable IgG antibody titres by day 365. Avidity and neutralisation functions of the anti-rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP antibodies peaked at day 28 and were maintained by day 365. INTERPRETATION: The replication and shedding do not affect the favourable risk-benefit balance of the rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP in children.
Authors
Alabi A, Kokou K, Mahmoudou S, Kavishna R, Nakka SS
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Microbiology or Immunology
Lista de serviços
-
Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.
-
Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.
-
Network Medicine: Methods and ApplicationsNetwork Medicine: Methods and Applications
-
ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.
-
Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.
-
Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.
-
In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.
-
The evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseasesThe evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseases
-
Network vaccinology.Network vaccinology.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammationPyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammation
-
Transcriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patientsTranscriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patients
-
Gene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian BrazilGene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian Brazil
-
In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.
-
Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.
-
Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.
-
Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.