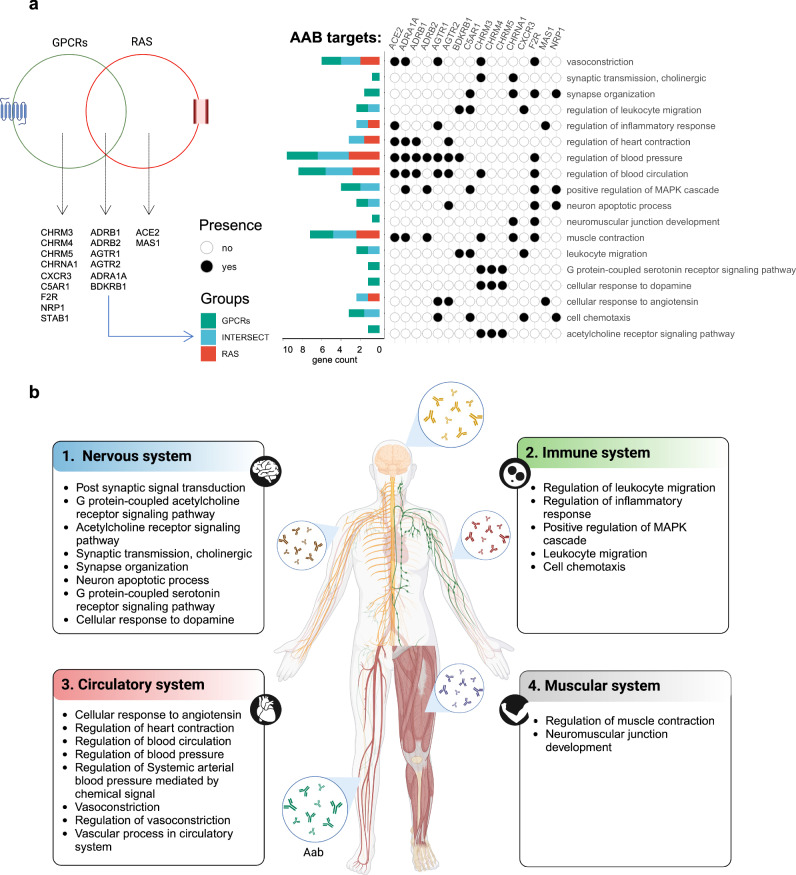
Dysregulated autoantibodies targeting AGTR1 are associated with the accumulation of COVID-19 symptoms.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) presents a wide spectrum of symptoms, the causes of which remain poorly understood. This study explored the associations between autoantibodies (AABs), particularly those targeting G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and renin‒angiotensin system (RAS) molecules, and the clinical manifestations of COVID-19. Using a cross-sectional analysis of 244 individuals, we applied multivariate analysis of variance, principal component analysis, and multinomial regression to examine the relationships between AAB levels and key symptoms. Significant correlations were identified between specific AABs and symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, anosmia, and dysgeusia. Notably, anti-AGTR1 antibodies, which contribute to endothelial glycocalyx (eGC) degradation, a process reversed by losartan, have emerged as strong predictors of core symptoms. AAB levels increased with symptom accumulation, peaking in patients exhibiting all four key symptoms. These findings highlight the role of AABs, particularly anti-AGTR1 antibodies, in determining symptom severity and suggest their involvement in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, including vascular complications.
Authors
Fonseca DLM, Jäpel M, Gyamfi MA, Filgueiras IS, Baiochi GC, et al.
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.Gene regulatory and signaling networks exhibit distinct topological distributions of motifs.
-
Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.Gene signatures of autopsy lungs from obese patients with COVID-19.
-
Network Medicine: Methods and ApplicationsNetwork Medicine: Methods and Applications
-
ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.ACE2 Expression Is Increased in the Lungs of Patients With Comorbidities Associated With Severe COVID-19.
-
Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.Drug repositioning for psychiatric and neurological disorders through a network medicine approach.
-
Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.Linking proteomic alterations in schizophrenia hippocampus to NMDAr hypofunction in human neurons and oligodendrocytes.
-
In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.In-depth analysis of laboratory parameters reveals the interplay between sex, age, and systemic inflammation in individuals with COVID-19.
-
The evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseasesThe evolution of knowledge on genes associated with human diseases
-
Network vaccinology.Network vaccinology.
-
Pyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammationPyruvate kinase M2 mediates IL-17 signaling in keratinocytes driving psoriatic skin inflammation
-
Transcriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patientsTranscriptome analysis of six tissues obtained post-mortem from sepsis patients
-
Gene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian BrazilGene Signatures of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Clinical-Immunological Profiles of Human Infection by Leishmania (L.) chagasi in Amazonian Brazil
-
In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.In vitro morphological profiling of T cells predicts clinical response to natalizumab therapy in patients with multiple sclerosis.
-
Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.Integrative immunology identified interferome signatures in uveitis and systemic disease-associated uveitis.
-
Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.Gene regulatory networks analysis for the discovery of prognostic genes in gliomas.
-
Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.Revealing shared molecular drivers of brain metastases from distinct primary tumors.