Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approach
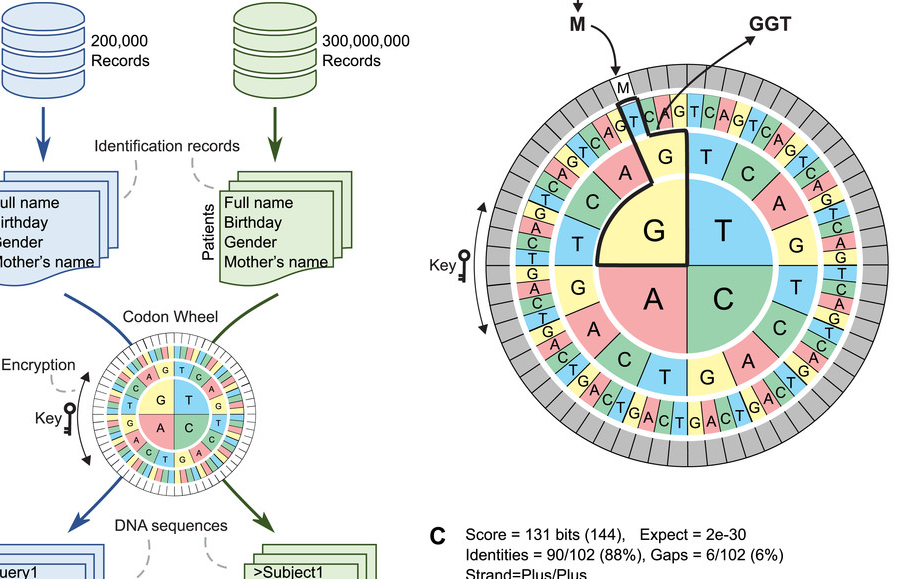
Background. Public health research frequently requires the integration of information from different data sources. However, errors in the records and the high computational costs involved make linking large administrative databases using record linkage (RL) methodologies a major challenge. Methods. We present Tucuxi-BLAST, a versatile tool for probabilistic RL that utilizes a DNA-encoded approach to encrypt, analyze and link massive administrative databases. Tucuxi-BLAST encodes the identification records into DNA. BLASTn algorithm is then used to align the sequences between databases. We tested and benchmarked on a simulated database containing records for 300 million individuals and also on four large administrative databases containing real data on Brazilian patients. Results. Our method was able to overcome misspellings and typographical errors in administrative databases. In processing the RL of the largest simulated dataset (200k records), the state-of-the-art method took 5 days and 7 h to perform the RL, while Tucuxi-BLAST only took 23 h. When compared with five existing RL tools applied to a gold-standard dataset from real health-related databases, Tucuxi-BLAST had the highest accuracy and speed. By repurposing genomic tools, Tucuxi-BLAST can improve data-driven medical research and provide a fast and accurate way to link individual information across several administrative databases.
Authors
Araujo, Jose Deney; Santos-e-Silva, Juan Carlo; Costa-Martins, Andre Guilherme; Sampaio, Vanderson; de Castro, Daniel Barros; de Souza, Robson F; Giddaluru, Jeevan; Ramos, Pablo Ivan P; Pita, Robespierre; Barreto, Mauricio L;
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
User-friendly computational Tools
Lista de serviços
-
StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.
-
CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.
-
webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.
-
Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.
-
Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.
-
OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.
-
Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.
-
Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.
-
Automatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone imagesAutomatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone images
-
Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approachTucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approach
-
Ten quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biologyTen quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biology