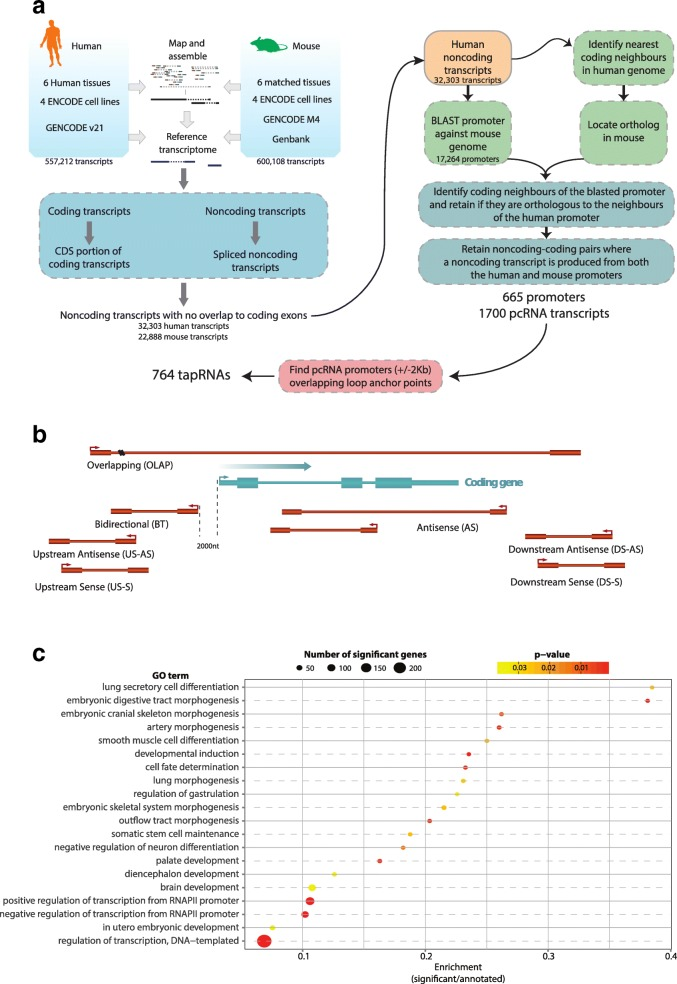
Genomic positional conservation identifies topological anchor point RNAs linked to developmental loci.
The mammalian genome is transcribed into large numbers of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), but the definition of functional lncRNA groups has proven difficult, partly due to their low sequence conservation and lack of identified shared properties. Here we consider promoter conservation and positional conservation as indicators of functional commonality. We identify 665 conserved lncRNA promoters in mouse and human that are preserved in genomic position relative to orthologous coding genes. These positionally conserved lncRNA genes are primarily associated with developmental transcription factor loci with which they are coexpressed in a tissue-specific manner. Over half of positionally conserved RNAs in this set are linked to chromatin organization structures, overlapping binding sites for the CTCF chromatin organiser and located at chromatin loop anchor points and borders of topologically associating domains (TADs). We define these RNAs as topological anchor point RNAs (tapRNAs). Characterization of these noncoding RNAs and their associated coding genes shows that they are functionally connected: they regulate each other's expression and influence the metastatic phenotype of cancer cells in vitro in a similar fashion. Furthermore, we find that tapRNAs contain conserved sequence domains that are enriched in motifs for zinc finger domain-containing RNA-binding proteins and transcription factors, whose binding sites are found mutated in cancers. This work leverages positional conservation to identify lncRNAs with potential importance in genome organization, development and disease. The evidence that many developmental transcription factors are physically and functionally connected to lncRNAs represents an exciting stepping-stone to further our understanding of genome regulation.
Authors
Paulo P Amaral; Tommaso Leonardi; Namshik Han; Emmanuelle Viré; Dennis K Gascoigne; Raúl Arias-Carrasco; Magdalena Büscher; Luca Pandolfini; Anda Zhang; Stefano Pluchino; Vinicius Maracaja-Coutinho; Helder I Nakaya; Martin Hemberg; Ramin Shiekhattar; Anton J Enright; Tony Kouzarides
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Integrative Biology
Lista de serviços
-
StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.
-
CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.
-
webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.
-
Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.
-
Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.
-
OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.
-
Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.
-
Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.
-
Automatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone imagesAutomatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone images
-
Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approachTucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approach
-
Ten quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biologyTen quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biology