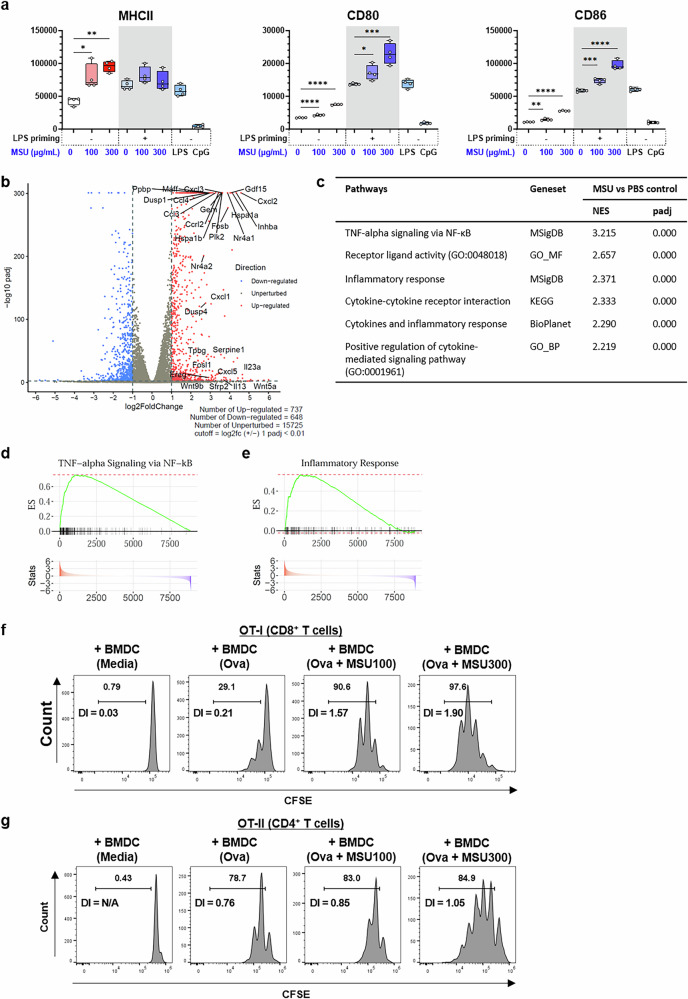
Emulsion adjuvant-induced uric acid release modulates optimal immunogenicity by targeting dendritic cells and B cells.
Squalene-based emulsion (SE) adjuvants like MF59 and AS03 are used in protein subunit vaccines against influenza virus (e.g., Fluad, Pandemrix, Arepanrix) and SARS-CoV-2 (e.g., Covifenz, SKYCovione). We demonstrate the critical role of uric acid (UA), a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), in triggering immunogenicity by SE adjuvants. In mice, SE adjuvants elevated DAMP levels in draining lymph nodes. Strikingly, inhibition of UA synthesis reduced vaccine-induced innate immunity, subsequently impairing optimal antibody and T cell responses. In vivo treatment with UA crystals elicited partial adjuvant effects. In vitro stimulation with UA crystals augmented the activation of dendritic cells (DCs) and B cells and altered multiple pathways in these cells, including inflammation and antigen presentation in DCs and cell proliferation in B cells. In an influenza vaccine model, UA contributed to protection against influenza viral infection. These results demonstrate the importance of DAMPs, specifically the versatile role of UA in the immunogenicity of SE adjuvants, by regulating DCs and B cells
Authors
Lee SM, Lee J, Kim DI, Avila JP, Nakaya H, et al.
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Vaccinology
Lista de serviços
-
StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.StructRNAfinder: an automated pipeline and web server for RNA families prediction.
-
CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.CEMiTool: a Bioconductor package for performing comprehensive modular co-expression analyses.
-
webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.webCEMiTool: Co-expression Modular Analysis Made Easy.
-
Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.Assessing the Impact of Sample Heterogeneity on Transcriptome Analysis of Human Diseases Using MDP Webtool.
-
Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.Predicting RNA Families in Nucleotide Sequences Using StructRNAfinder.
-
OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.OUTBREAK: a user-friendly georeferencing online tool for disease surveillance.
-
Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.Noninvasive prenatal paternity determination using microhaplotypes: a pilot study.
-
Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.Editorial: User-Friendly Tools Applied to Genetics or Systems Biology.
-
Automatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone imagesAutomatic detection of the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi in blood smears using a machine learning approach applied to mobile phone images
-
Tucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approachTucuxi-BLAST: Enabling fast and accurate record linkage of large-scale health-related administrative databases through a DNA-encoded approach
-
Ten quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biologyTen quick tips for harnessing the power of ChatGPT in computational biology