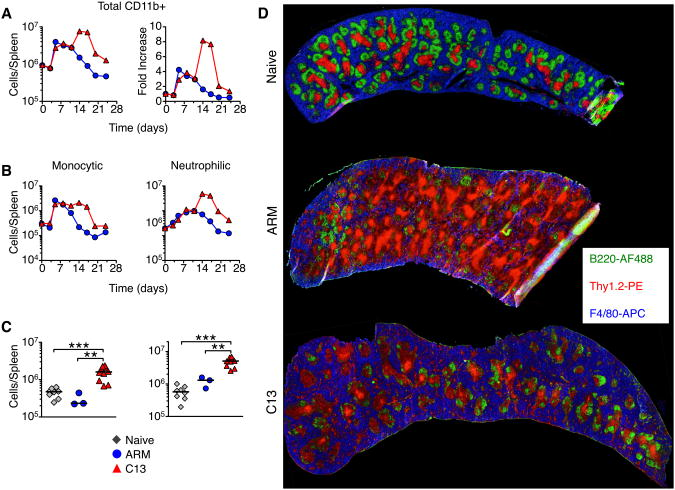
Chronic but not acute virus infection induces sustained expansion of myeloid suppressor cell numbers that inhibit viral-specific T cell immunity.
Resolution of acute and chronic viral infections requires activation of innate cells to initiate and maintain adaptive immune responses. Here we report that infection with acute Armstrong (ARM) or chronic Clone 13 (C13) strains of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) led to two distinct phases of innate immune response. During the first 72 hr of infection, dendritic cells upregulated activation markers and stimulated antiviral CD8(+) T cells, independent of viral strain. Seven days after infection, there was an increase in Ly6C(hi) monocytic and Gr-1(hi) neutrophilic cells in lymphoid organs and blood. This expansion in cell numbers was enhanced and sustained in C13 infection, whereas it occurred only transiently with ARM infection. These cells resembled myeloid-derived suppressor cells and potently suppressed T cell proliferation. The reduction of monocytic cells in Ccr2(-/-) mice or after Gr-1 antibody depletion enhanced antiviral T cell function. Thus, innate cells have an important immunomodulatory role throughout chronic infection.
Authors
Brian A Norris; Luke S Uebelhoer; Helder I Nakaya; Aryn A Price; Arash Grakoui; Bali Pulendran
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Microbiology or Immunology
Lista de serviços
-
RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.
-
Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.
-
Concepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome AnalysesConcepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome Analyses
-
The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.
-
Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.
-
The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.
-
Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.
-
Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.
-
São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.
-
A reasonable request for true data sharing.A reasonable request for true data sharing.