Integration of miRNA and gene expression profiles suggest a role for miRNAs in the pathobiological processes of acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection.
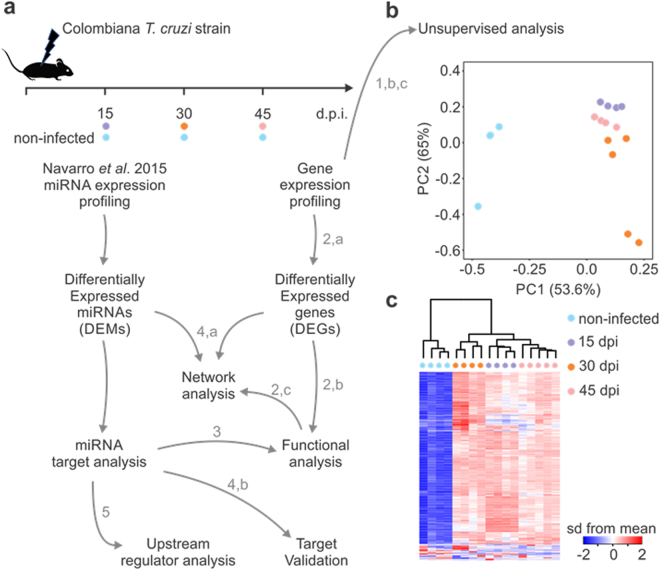
Chagas disease, caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, is endemic in Latin America. Its acute phase is associated with high parasitism, myocarditis and profound myocardial gene expression changes. A chronic phase ensues where 30% develop severe heart lesions. Mouse models of T. cruzi infection have been used to study heart damage in Chagas disease. The aim of this study was to provide an interactome between miRNAs and their targetome in Chagas heart disease by integrating gene and microRNA expression profiling data from hearts of T. cruzi infected mice. Gene expression profiling revealed enrichment in biological processes and pathways associated with immune response and metabolism. Pathways, functional and upstream regulator analysis of the intersections between predicted targets of differentially expressed microRNAs and differentially expressed mRNAs revealed enrichment in biological processes and pathways such as IFNγ, TNFα, NF-kB signaling signatures, CTL-mediated apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and Nrf2-modulated antioxidative responses. We also observed enrichment in other key heart disease-related processes like myocarditis, fibrosis, hypertrophy and arrhythmia. Our correlation study suggests that miRNAs may be implicated in the pathophysiological processes taking place the hearts of acutely T. cruzi-infected mice.
Authors
Ludmila Rodrigues Pinto Ferreira; Frederico Moraes Ferreira; Laurie Laugier; Sandrine Cabantous; Isabela Cunha Navarro; Darlan da Silva Cândido; Vagner Carvalho Rigaud; Juliana Monte Real; Glaucia Vilar Pereira; Isabela Resende Pereira; Leonardo Ruivo; Ramendra Pati Pandey; Marilda Savoia; Jorge Kalil; Joseli Lannes-Vieira; Helder Nakaya; Christophe Chevillard; Edecio Cunha-Neto
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Integrative Biology
Lista de serviços
-
RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.
-
Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.
-
Concepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome AnalysesConcepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome Analyses
-
The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.
-
Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.
-
The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.
-
Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.
-
Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.
-
São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.
-
A reasonable request for true data sharing.A reasonable request for true data sharing.