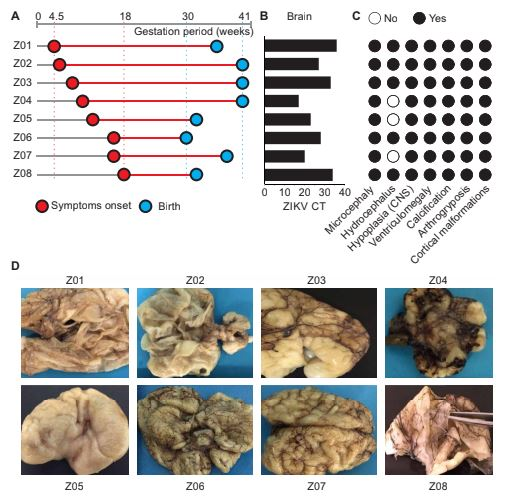
Molecular alterations in the extracellular matrix in the brains of newborns with congenital Zika syndrome.
Zika virus (ZIKV) infection during pregnancy can cause a set of severe abnormalities in the fetus known as congenital Zika syndrome (CZS). Experiments with animal models and in vitro systems have substantially contributed to our understanding of the pathophysiology of ZIKV infection. Here, to investigate the molecular basis of CZS in humans, we used a systems biology approach to integrate transcriptomic, proteomic, and genomic data from the postmortem brains of neonates with CZS. We observed that collagens were greatly reduced in expression in CZS brains at both the RNA and protein levels and that neonates with CZS had several single-nucleotide polymorphisms in collagen-encoding genes that are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta and arthrogryposis. These findings were validated by immunohistochemistry and comparative analysis of collagen abundance in ZIKV-infected and uninfected samples. In addition, we showed a ZIKV-dependent increase in the expression of cell adhesion factors that are essential for neurite outgrowth and axon guidance, findings that are consistent with the neuronal migration defects observed in CZS. Together, these findings provide insights into the underlying molecular alterations in the ZIKV-infected brain and reveal host genes associated with CZS susceptibility.
Authors
Renato S Aguiar; Fabio Pohl; Guilherme L Morais; Fabio C S Nogueira; Joseane B Carvalho; Letícia Guida; Luis W P Arge; Adriana Melo; Maria E L Moreira; Daniela P Cunha; Leonardo Gomes; Elyzabeth A Portari; Erika Velasquez; Rafael D Melani; Paula Pezzuto; Fernanda L de Castro; Victor E V Geddes; Alexandra L Gerber; Girlene S Azevedo; Bruno L Schamber-Reis; Alessandro L Gonçalves; Inácio Junqueira-de-Azevedo; Milton Y Nishiyama; Paulo L Ho; Alessandra S Schanoski; Viviane Schuch; Amilcar Tanuri; Leila Chimelli; Zilton F M Vasconcelos; Gilberto B Domont; Ana T R Vasconcelos; Helder I Nakaya
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.RASL11A, member of a novel small monomeric GTPase gene family, is down-regulated in prostate tumors.
-
Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.Splice variants of TLE family genes and up-regulation of a TLE3 isoform in prostate tumors.
-
Concepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome AnalysesConcepts on Microarray Design for Genome and Transcriptome Analyses
-
The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.The iron stimulon of Xylella fastidiosa includes genes for type IV pilus and colicin V-like bacteriocins.
-
Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.Origins of the Xylella fastidiosa prophage-like regions and their impact in genome differentiation.
-
The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.The role of prophage in plant-pathogenic bacteria.
-
Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.Genetic control of immune response and susceptibility to infectious diseases.
-
Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.Building capacity for advances in tuberculosis research; proceedings of the third RePORT international meeting.
-
São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.São Paulo School of Advanced Sciences on Vaccines: an overview.
-
A reasonable request for true data sharing.A reasonable request for true data sharing.