Daily Rhythms of TNFα Expression and Food Intake Regulate Synchrony of Plasmodium Stages with the Host Circadian Cycle.
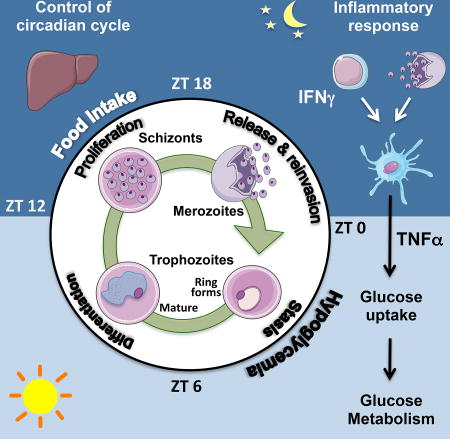
The Plasmodium cell cycle, wherein millions of parasites differentiate and proliferate, occurs in synchrony with the vertebrate host's circadian cycle. The underlying mechanisms are unknown. Here we addressed this question in a mouse model of Plasmodium chabaudi infection. Inflammatory gene expression and carbohydrate metabolism are both enhanced in interferon-γ (IFNγ)-primed leukocytes and liver cells from P. chabaudi-infected mice. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) expression oscillates across the host circadian cycle, and increased TNFα correlates with hypoglycemia and a higher frequency of non-replicative ring forms of trophozoites. Conversely, parasites proliferate and acquire biomass during food intake by the host. Importantly, cyclic hypoglycemia is attenuated and synchronization of P. chabaudi stages is disrupted in IFNγ -/- , TNF receptor -/- , or diabetic mice. Hence, the daily rhythm of systemic TNFα production and host food intake set the pace for Plasmodium synchronization with the host's circadian cycle. This mechanism indicates that Plasmodium parasites take advantage of the host's feeding habits.
Authors
Isabella Cristina Hirako; Patrícia Aparecida Assis; Natália Satchiko Hojo-Souza; George Reed; Helder Nakaya; Douglas Taylor Golenbock; Roney Santos Coimbra; Ricardo Tostes Gazzinelli
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
As antisense RNA gets intronic.As antisense RNA gets intronic.
-
Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.
-
Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.
-
The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.
-
Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.
-
Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.
-
Long non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunityLong non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunity
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophagesComparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophages
-
SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.