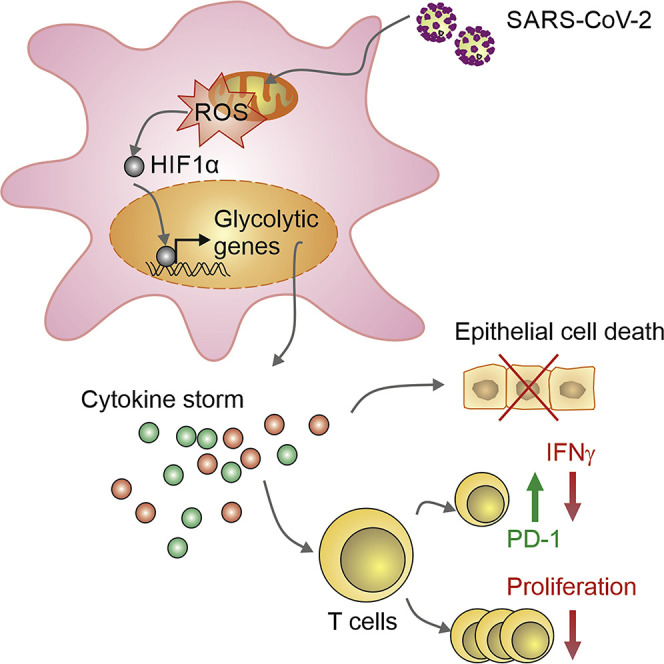
Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1α/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis.
COVID-19 can result in severe lung injury. It remained to be determined why diabetic individuals with uncontrolled glucose levels are more prone to develop the severe form of COVID-19. The molecular mechanism underlying SARS-CoV-2 infection and what determines the onset of the cytokine storm found in severe COVID-19 patients are unknown. Monocytes and macrophages are the most enriched immune cell types in the lungs of COVID-19 patients and appear to have a central role in the pathogenicity of the disease. These cells adapt their metabolism upon infection and become highly glycolytic, which facilitates SARS-CoV-2 replication. The infection triggers mitochondrial ROS production, which induces stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and consequently promotes glycolysis. HIF-1α-induced changes in monocyte metabolism by SARS-CoV-2 infection directly inhibit T cell response and reduce epithelial cell survival. Targeting HIF-1ɑ may have great therapeutic potential for the development of novel drugs to treat COVID-19.
Authors
Ana Campos Codo; Gustavo Gastão Davanzo; Lauar de Brito Monteiro; Gabriela Fabiano de Souza; Stéfanie Primon Muraro; João Victor Virgilio-da-Silva; Juliana Silveira Prodonoff; Victor Corasolla Carregari; Carlos Alberto Oliveira de Biagi Junior; Fernanda Crunfli; Jeffersson Leandro Jimenez Restrepo; Pedro Henrique Vendramini; Guilherme Reis-de-Oliveira; Karina Bispo Dos Santos; Daniel A Toledo-Teixeira; Pierina Lorencini Parise; Matheus Cavalheiro Martini; Rafael Elias Marques; Helison R Carmo; Alexandre Borin; Laís Durço Coimbra; Vinícius O Boldrini; Natalia S Brunetti; Andre S Vieira; Eli Mansour; Raisa G Ulaf; Ana F Bernardes; Thyago A Nunes; Luciana C Ribeiro; Andre C Palma; Marcus V Agrela; Maria Luiza Moretti; Andrei C Sposito; Fabrício Bíscaro Pereira; Licio Augusto Velloso; Marco Aurélio Ramirez Vinolo; André Damasio; José Luiz Proença-Módena; Robson Francisco Carvalho; Marcelo A Mori; Daniel Martins-de-Souza; Helder I Nakaya; Alessandro S Farias; Pedro M Moraes-Vieira
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
As antisense RNA gets intronic.As antisense RNA gets intronic.
-
Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.
-
Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.
-
The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.
-
Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.
-
Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.
-
Long non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunityLong non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunity
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophagesComparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophages
-
SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.