Activation of the IDO1-GCN2-ATF4-CHOP Pathway During the Massive Generation of Antibody-Secreting Cells in Dengue Patients Through Single-Cell Transcriptomics.
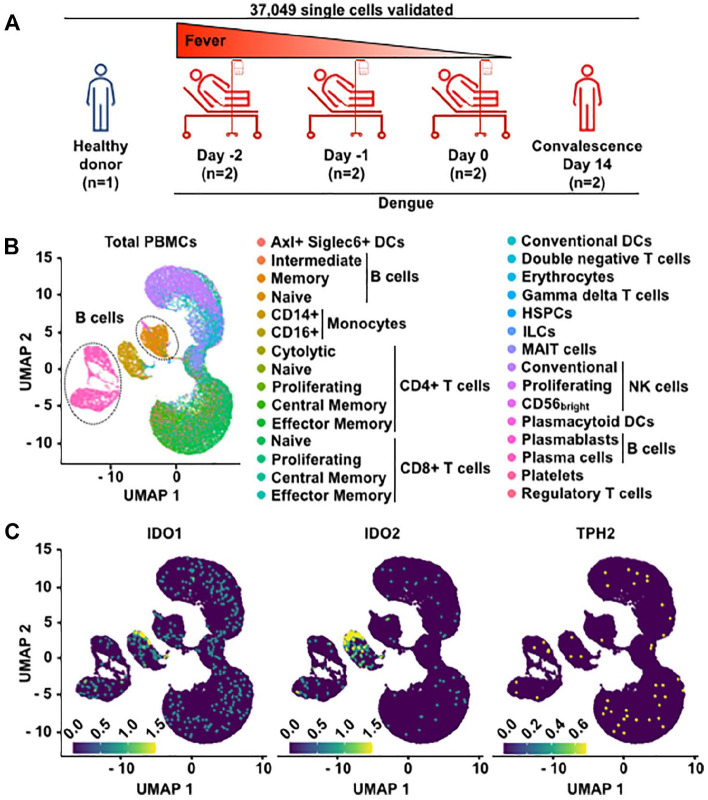
Dengue, a widespread mosquito-borne disease, annually afflicts millions globally, posing substantial mortality risks. Preceding disease defervescence, a marked and transient surge in antibody-secreting cell (ASC) frequency correlates with disease severity, paralleled by heightened tryptophan degradation. Investigating details of this process through single-cell transcriptomics from public repositories, our data pinpoint CD14+ monocytes as principal IDO1 and IDO2 expressors, implicating them, rather than B cells, in initiating tryptophan metabolism. Interestingly, naive B cells exhibit altered gene expression indicative of early impact by tryptophan deficiency before defervescence with a potential impact on the B cell fate. Dengue-induced ASCs upregulated GCN2, PERK, eIF2a, ATF4 genes as well as BIM and CASP-3. However, the high expression of anti-apoptotic genes (FKBP8 [a CHOP-regulated gene], BCL-XL, BCL-2, MCL-1) allows enhanced ASC survival. Proliferation and differentiation-related genes (eIF4EBP1, RRM2, and HIF1a) were also upregulated in ASCs. These findings untangle how Dengue modulates the host metabolism and B-cell responses, although further research is needed to fully understand their implications on disease progression.
Authors
Nascimento JC, Gonçalves ANA, Akashi KT, Nakaya HI, et al.
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
Chapter 15 - Systems Biology of Infectious Diseases and VaccinesChapter 15 - Systems Biology of Infectious Diseases and Vaccines
-
Synergy of Omeprazole and Praziquantel In Vitro Treatment against Schistosoma mansoni Adult Worms.Synergy of Omeprazole and Praziquantel In Vitro Treatment against Schistosoma mansoni Adult Worms.
-
Systems Immunology of Diabetes-Tuberculosis Comorbidity Reveals Signatures of Disease Complications.Systems Immunology of Diabetes-Tuberculosis Comorbidity Reveals Signatures of Disease Complications.
-
Systems ImmunologySystems Immunology
-
Gene profiling of Chikungunya virus arthritis in a mouse model reveals significant overlap with rheumatoid arthritis.Gene profiling of Chikungunya virus arthritis in a mouse model reveals significant overlap with rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Toward an Integrated View of Operational Tolerance in Human Renal Transplantation: A Systems Biology Perspective.Toward an Integrated View of Operational Tolerance in Human Renal Transplantation: A Systems Biology Perspective.
-
Total parasite biomass but not peripheral parasitaemia is associated with endothelial and haematological perturbations in Plasmodium vivax patientsTotal parasite biomass but not peripheral parasitaemia is associated with endothelial and haematological perturbations in Plasmodium vivax patients
-
Acid pH Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Risk of Death by COVID-19Acid pH Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Risk of Death by COVID-19
-
The relationship between cytokine and neutrophil gene network distinguishes SARS-CoV-2-infected patients by sex and age.The relationship between cytokine and neutrophil gene network distinguishes SARS-CoV-2-infected patients by sex and age.
-
Immature neutrophil signature associated with the sexual dimorphism of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Immature neutrophil signature associated with the sexual dimorphism of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
-
Platelet disturbances correlate with endothelial cell activation in uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria.Platelet disturbances correlate with endothelial cell activation in uncomplicated Plasmodium vivax malaria.
-
miRNAs may play a major role in the control of gene expression in key pathobiological processes in Chagas disease cardiomyopathy.miRNAs may play a major role in the control of gene expression in key pathobiological processes in Chagas disease cardiomyopathy.
-
Zika virus infection and cytokines.Zika virus infection and cytokines.
-
Systems immunology of flavivirus infection.Systems immunology of flavivirus infection.
-
Kdm6b Regulates the Generation of Effector CD8 + T Cells by Inducing Chromatin Accessibility in Effector-Associated GenesKdm6b Regulates the Generation of Effector CD8 + T Cells by Inducing Chromatin Accessibility in Effector-Associated Genes
-
Neonatal T Follicular Helper Cells Are Lodged in a Pre-T Follicular Helper Stage Favoring Innate Over Adaptive Germinal Center Responses.Neonatal T Follicular Helper Cells Are Lodged in a Pre-T Follicular Helper Stage Favoring Innate Over Adaptive Germinal Center Responses.
-
Exacerbation of Chikungunya Virus Rheumatic Immunopathology by a High Fiber Diet and Butyrate.Exacerbation of Chikungunya Virus Rheumatic Immunopathology by a High Fiber Diet and Butyrate.
-
Severe COVID-19 shares a common neutrophil activation signature with other acute inflammatory statesSevere COVID-19 shares a common neutrophil activation signature with other acute inflammatory states
-
Efferocytosis of SARS-CoV-2-infected dying cells impairs macrophage anti-inflammatory functions and clearance of apoptotic cellsEfferocytosis of SARS-CoV-2-infected dying cells impairs macrophage anti-inflammatory functions and clearance of apoptotic cells
-
Daily Rhythms of TNFα Expression and Food Intake Regulate Synchrony of Plasmodium Stages with the Host Circadian Cycle.Daily Rhythms of TNFα Expression and Food Intake Regulate Synchrony of Plasmodium Stages with the Host Circadian Cycle.
-
Discordant congenital Zika syndrome twins show differential in vitro viral susceptibility of neural progenitor cells.Discordant congenital Zika syndrome twins show differential in vitro viral susceptibility of neural progenitor cells.
-
Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1α/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis.Elevated Glucose Levels Favor SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Monocyte Response through a HIF-1α/Glycolysis-Dependent Axis.
-
Systems analysis of subjects acutely infected with the Chikungunya virus.Systems analysis of subjects acutely infected with the Chikungunya virus.
-
Molecular alterations in the extracellular matrix in the brains of newborns with congenital Zika syndrome.Molecular alterations in the extracellular matrix in the brains of newborns with congenital Zika syndrome.
-
Inflammation induced by influenza virus impairs human innate immune control of pneumococcus.Inflammation induced by influenza virus impairs human innate immune control of pneumococcus.
-
Tissue-resident glial cells associate with tumoral vasculature and promote cancer progressionTissue-resident glial cells associate with tumoral vasculature and promote cancer progression
-
Increased mTOR Signaling and Impaired Autophagic Flux Are Hallmarks of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Increased mTOR Signaling and Impaired Autophagic Flux Are Hallmarks of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.
-
Chikungunya patient transcriptional signatures faithfully recapitulated in a C57BL/6J mouse modelChikungunya patient transcriptional signatures faithfully recapitulated in a C57BL/6J mouse model
-
Imbalanced IL-1B and IL-18 Expression in Sézary SyndromeImbalanced IL-1B and IL-18 Expression in Sézary Syndrome
-
C5aR1 signaling triggers lung immunopathology in COVID-19 through neutrophil extracellular trapsC5aR1 signaling triggers lung immunopathology in COVID-19 through neutrophil extracellular traps
-
Cutting Edge: Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 Subunit Cbx4 Positively Regulates Effector Responses in CD8 T CellsCutting Edge: Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 Subunit Cbx4 Positively Regulates Effector Responses in CD8 T Cells
-
COVID-19-related hyperglycemia is associated with infection of hepatocytes and stimulation of gluconeogenesisCOVID-19-related hyperglycemia is associated with infection of hepatocytes and stimulation of gluconeogenesis
-
Characteristics and anatomic location of PD-1(+)TCF1(+) stem-like CD8 T cells in chronic viral infection and cancerCharacteristics and anatomic location of PD-1(+)TCF1(+) stem-like CD8 T cells in chronic viral infection and cancer
-
Morphological, cellular, and molecular basis of brain infection in COVID-19 patientsMorphological, cellular, and molecular basis of brain infection in COVID-19 patients
-
The costimulatory molecule ICOS limits memory-like properties and function of exhausted PD-1(+)CD8(+) T cells.The costimulatory molecule ICOS limits memory-like properties and function of exhausted PD-1(+)CD8(+) T cells.
-
Activation of the IDO1-GCN2-ATF4-CHOP Pathway During the Massive Generation of Antibody-Secreting Cells in Dengue Patients Through Single-Cell Transcriptomics.Activation of the IDO1-GCN2-ATF4-CHOP Pathway During the Massive Generation of Antibody-Secreting Cells in Dengue Patients Through Single-Cell Transcriptomics.
-
Transcriptomic and Immunopathological Profiles of Inflammasomes in Different Clinical Forms of American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.Transcriptomic and Immunopathological Profiles of Inflammasomes in Different Clinical Forms of American Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.
-
Molecular Insights into Cell-Mediated Immunity in Atypical Non-Ulcerated Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.Molecular Insights into Cell-Mediated Immunity in Atypical Non-Ulcerated Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.
-
Transcriptomic insights into early mechanisms underlying post-chikungunya chronic inflammatory joint disease.Transcriptomic insights into early mechanisms underlying post-chikungunya chronic inflammatory joint disease.
-
Dysregulated autoantibodies targeting AGTR1 are associated with the accumulation of COVID-19 symptoms.Dysregulated autoantibodies targeting AGTR1 are associated with the accumulation of COVID-19 symptoms.
-
Editorial: Systems immunology to advance vaccine development.Editorial: Systems immunology to advance vaccine development.
-
Prion protein regulates invasiveness in glioblastoma stem cells.Prion protein regulates invasiveness in glioblastoma stem cells.
-
Systems Immunology Approaches to Understanding Immune Responses in Acute Infection of Yellow Fever Patients.Systems Immunology Approaches to Understanding Immune Responses in Acute Infection of Yellow Fever Patients.
-
Sex-Based Differences in Thyroid Plasma B Cell Infiltration: Implications for Autoimmune Disease Susceptibility.Sex-Based Differences in Thyroid Plasma B Cell Infiltration: Implications for Autoimmune Disease Susceptibility.
-
The single-cell transcriptome of mTECs and CD4(+) thymocytes under adhesion revealed heterogeneity of mTECs and a network controlled by Aire and lncRNAs.The single-cell transcriptome of mTECs and CD4(+) thymocytes under adhesion revealed heterogeneity of mTECs and a network controlled by Aire and lncRNAs.
-
Chikungunya-Driven Gene Expression Linked to Osteoclast Survival and Chronic Arthralgia.Chikungunya-Driven Gene Expression Linked to Osteoclast Survival and Chronic Arthralgia.
-
The global evolution and impact of systems biology and artificial intelligence in stem cell research and therapeutics development: a scoping review.The global evolution and impact of systems biology and artificial intelligence in stem cell research and therapeutics development: a scoping review.
-
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is associated with susceptibility to experimental pneumococcal challenge in older adults.Inflammation of the nasal mucosa is associated with susceptibility to experimental pneumococcal challenge in older adults.