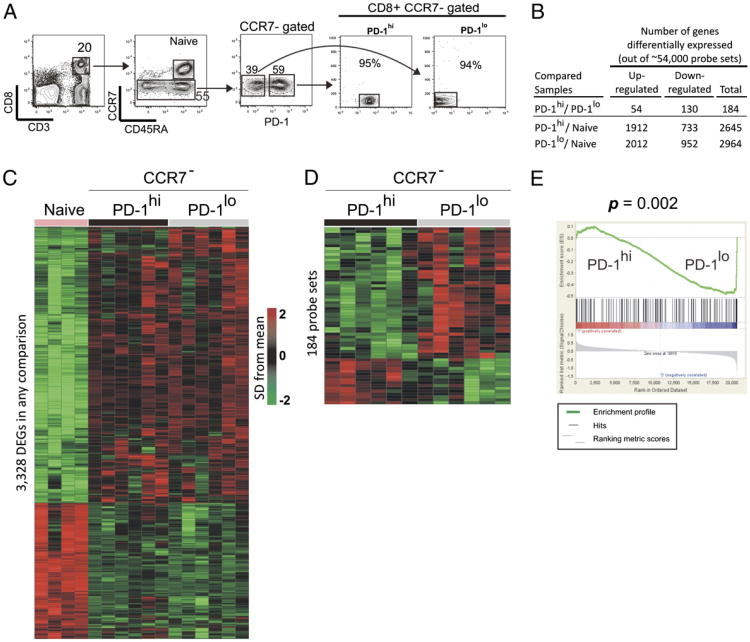
Phenotype, function, and gene expression profiles of programmed death-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy human adults.
T cell dysfunction is an important feature of many chronic viral infections. In particular, it was shown that programmed death-1 (PD-1) regulates T cell dysfunction during chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in mice, and PD-1(hi) cells exhibit an intense exhausted gene signature. These findings were extended to human chronic infections such as HIV, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis B virus. However, it is not known if PD-1(hi) cells of healthy humans have the traits of exhausted cells. In this study, we provide a comprehensive description of phenotype, function, and gene expression profiles of PD-1(hi) versus PD-1(lo) CD8 T cells in the peripheral blood of healthy human adults as follows: 1) the percentage of naive and memory CD8 T cells varied widely in the peripheral blood cells of healthy humans, and PD-1 was expressed by the memory CD8 T cells; 2) PD-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy humans did not significantly correlate with the PD-1(hi) exhausted gene signature of HIV-specific human CD8 T cells or chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific CD8 T cells from mice; 3) PD-1 expression did not directly affect the ability of CD8 T cells to secrete cytokines in healthy adults; 4) PD-1 was expressed by the effector memory compared with terminally differentiated effector CD8 T cells; and 5) finally, an interesting inverse relationship between CD45RA and PD-1 expression was observed. In conclusion, our study shows that most PD-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy adult humans are effector memory cells rather than exhausted cells.
Authors
Jaikumar Duraiswamy; Chris C Ibegbu; David Masopust; Joseph D Miller; Koichi Araki; Gregory H Doho; Pramila Tata; Satish Gupta; Michael J Zilliox; Helder I Nakaya; Bali Pulendran; W Nicholas Haining; Gordon J Freeman; Rafi Ahmed
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Microbiology or Immunology
Lista de serviços
-
Systems vaccinology: its promise and challenge for HIV vaccine development.Systems vaccinology: its promise and challenge for HIV vaccine development.
-
Systems vaccinology: learning to compute the behavior of vaccine induced immunity.Systems vaccinology: learning to compute the behavior of vaccine induced immunity.
-
Systems biology of vaccination in the elderly.Systems biology of vaccination in the elderly.
-
Immunity to viruses: learning from successful human vaccines.Immunity to viruses: learning from successful human vaccines.
-
Systems biological approaches to measure and understand vaccine immunity in humans.Systems biological approaches to measure and understand vaccine immunity in humans.
-
Gene signatures related to B-cell proliferation predict influenza vaccine-induced antibody response.Gene signatures related to B-cell proliferation predict influenza vaccine-induced antibody response.
-
Vaccinology in the era of high-throughput biology.Vaccinology in the era of high-throughput biology.
-
Systems vaccinology: Enabling rational vaccine design with systems biological approaches.Systems vaccinology: Enabling rational vaccine design with systems biological approaches.
-
Systems Vaccinology Applied to DNA Vaccines: Perspective and Challenges.Systems Vaccinology Applied to DNA Vaccines: Perspective and Challenges.
-
Adjuvanting a Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Vaccine with Toll-Like Receptor Ligands Encapsulated in Nanoparticles Induces Persistent Antibody Responses and Enhanced Protection in TRIM5α Restrictive Macaques.Adjuvanting a Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Vaccine with Toll-Like Receptor Ligands Encapsulated in Nanoparticles Induces Persistent Antibody Responses and Enhanced Protection in TRIM5α Restrictive Macaques.
-
Methods for predicting vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity.Methods for predicting vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity.
-
Antigenicity prediction and vaccine recommendation of human influenza virus A (H3N2) using convolutional neural networks.Antigenicity prediction and vaccine recommendation of human influenza virus A (H3N2) using convolutional neural networks.
-
Pneumococcal colonization impairs mucosal immune responses to live attenuated influenza vaccine.Pneumococcal colonization impairs mucosal immune responses to live attenuated influenza vaccine.
-
Human Transcriptomic Response to the VSV-Vectored Ebola Vaccine.Human Transcriptomic Response to the VSV-Vectored Ebola Vaccine.
-
Induction of Cell Cycle and NK Cell Responses by Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines against Typhoid Fever.Induction of Cell Cycle and NK Cell Responses by Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines against Typhoid Fever.
-
Systems Biology Analysis of the Radiation-Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine Reveals a Role for Growth Factors in Protection and Hemostasis Inhibition in Parasite Survival.Systems Biology Analysis of the Radiation-Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine Reveals a Role for Growth Factors in Protection and Hemostasis Inhibition in Parasite Survival.
-
Molecular alterations in human milk in simulated maternal nasal mucosal infection with live attenuated influenza vaccinationMolecular alterations in human milk in simulated maternal nasal mucosal infection with live attenuated influenza vaccination
-
Systems biology of immunity to MF59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines in early childhood.Systems biology of immunity to MF59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines in early childhood.
-
Systems analysis of protective immune responses to RTS,S malaria vaccination in humans.Systems analysis of protective immune responses to RTS,S malaria vaccination in humans.
-
Systems vaccinology.Systems vaccinology.
-
Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans.Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans.
-
Systems biology of vaccination for seasonal influenza in humans.Systems biology of vaccination for seasonal influenza in humans.
-
Prior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in childrenPrior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in children
-
Systems Analysis of Immunity to Influenza Vaccination across Multiple Years and in Diverse Populations Reveals Shared Molecular Signatures.Systems Analysis of Immunity to Influenza Vaccination across Multiple Years and in Diverse Populations Reveals Shared Molecular Signatures.
-
Molecular signatures of antibody responses derived from a systems biology study of five human vaccines.Molecular signatures of antibody responses derived from a systems biology study of five human vaccines.
-
Long noncoding RNAs are involved in multiple immunological pathways in response to vaccination.Long noncoding RNAs are involved in multiple immunological pathways in response to vaccination.
-
Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans.Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans.
-
Hidden in plain sight: uncovering the role of CREB1 in HIV-1 vaccine-induced immunityHidden in plain sight: uncovering the role of CREB1 in HIV-1 vaccine-induced immunity
-
Transcriptomic signatures induced by the Ebola virus vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV-GP in adult cohorts in Europe, Africa, and North America: a molecular biomarker studyTranscriptomic signatures induced by the Ebola virus vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV-GP in adult cohorts in Europe, Africa, and North America: a molecular biomarker study
-
Baseline gene signatures of reactogenicity to Ebola vaccination: a machine learning approach across multiple cohortsBaseline gene signatures of reactogenicity to Ebola vaccination: a machine learning approach across multiple cohorts
-
Global blood miRNA profiling unravels early signatures of immunogenicity of Ebola vaccine rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GPGlobal blood miRNA profiling unravels early signatures of immunogenicity of Ebola vaccine rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP
-
COVID-19 vaccination atlas using an integrative systems vaccinology approach.COVID-19 vaccination atlas using an integrative systems vaccinology approach.
-
Emulsion adjuvant-induced uric acid release modulates optimal immunogenicity by targeting dendritic cells and B cells.Emulsion adjuvant-induced uric acid release modulates optimal immunogenicity by targeting dendritic cells and B cells.
-
System vaccinology analysis of predictors and mechanisms of antibody response durability to multiple vaccines in humans.System vaccinology analysis of predictors and mechanisms of antibody response durability to multiple vaccines in humans.
-
Poly I:C elicits broader and stronger humoral and cellular responses to a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein malaria vaccine than Alhydrogel in mice.Poly I:C elicits broader and stronger humoral and cellular responses to a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein malaria vaccine than Alhydrogel in mice.