HIV infection increases the risk of acquiring Plasmodium vivax malaria: a 4-year cohort study in the Brazilian Amazon HIV and risk of vivax malaria
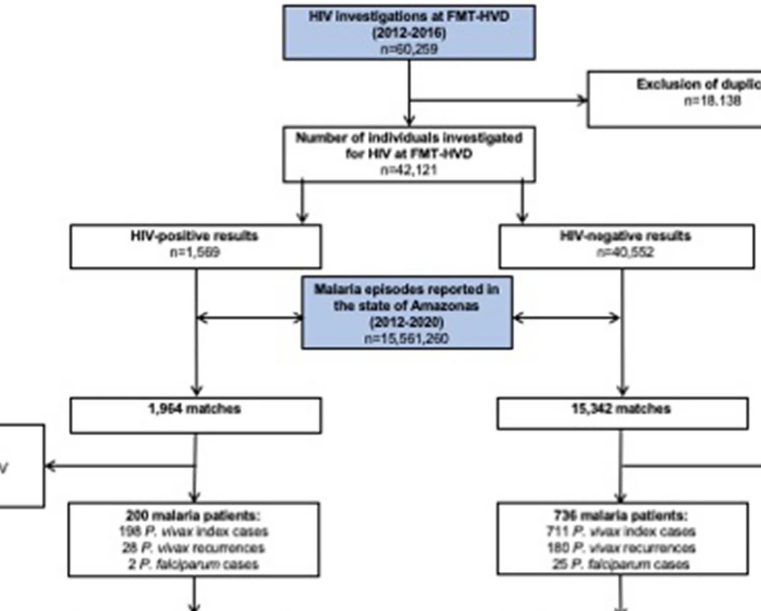
Globally, malaria and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are both independently associated with a massive burden of disease and death. While their co-infection has been well studied for Plasmodium falciparum, scarce data exist regarding the association of P. vivax and HIV. In this cohort study, we assessed the effect of HIV on the risk of vivax malaria infection and recurrence during a 4-year follow-up period in an endemic area of the Brazilian Amazon. For the purpose of this study, we obtained clinical information from January 2012 to December 2016 from two databases. HIV screening data were acquired from the clinical information system at the tropical hospital Fundação de Medicina Tropical Dr. Heitor Vieira Dourado (FMT-HVD). The National Malaria Surveillance database (SIVEP malaria) was utilized to identify malaria infections during a 4-year follow-up period after diagnosis of HIV. Both datasets were combined via data linkage. Between 2012 and 2016, a total of 42,121 people were screened for HIV, with 1569 testing positive (3.7%). Out of all the patients diagnosed with HIV, 198 had at least one episode of P. vivax malaria in the follow-up. In the HIV-negative group, 711 participants had at least one P. vivax malaria episode. When comparing both groups, HIV patients had a 6.48 [(5.37–7.83); P < 0.0001] (adjusted relative risk) greater chance of acquiring P. vivax malaria. Moreover, being of the male gender [ARR = 1.41 (1.17–1.71); P < 0.0001], Amerindian ethnicity [ARR = 2.77 (1.46–5.28); P < 0.0001], and a resident in a municipality of the Metropolitan region of Manaus [ARR = 1.48 (1.02–2.15); P = 0.038] were independent risk factors associated with an increased risk of clinical malaria. Education ≥ 8 years [ARR = 0.41 (0.26–0.64); P < 0.0001] and living in the urban area [ARR = 0.44 (0.24–0.80); P = 0.007] were associated to a lower risk of P. vivax malaria. A total of 28 (14.1%) and 180 (25.3%) recurrences (at least a second clinical malaria episode) were reported in the HIV-positive and HIV-negative groups, respectively. After adjusting for sex and education, HIV-positive status was associated with a tendency towards protection from P. vivax malaria recurrences [ARR = 0.55 (0.27–1.10); P = 0.090]. HIV status was not associated with hospitalizations due to P. vivax malaria. CD4 + counts and viral load were not associated with recurrences of P. vivax malaria. No significant differences were found in the distribution of parasitemia between HIV-negative and HIV-positive P. vivax malaria patients. Our results suggest that HIV-positive status is a risk factor for vivax malaria infection, which represents an additional challenge that should be addressed during elimination efforts.
Authors
Guerra, Cecilia Victoria Caraballo; da Silva, Bernardo Maia; Mi¼ller, Pia; Baia-da-Silva, Djane Clarys; Moura, Marco Antonio Saboia; Araiuo, Jose Deney Alves; Silva-Neto, Alexandre Vilhena; da Silva Balieiro, Antonio Alcirley; da Costa-Martins, Andre Guilherme; Melo, Gisely Cardoso;
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Digital Epidemiology
Lista de serviços
-
Systems vaccinology: its promise and challenge for HIV vaccine development.Systems vaccinology: its promise and challenge for HIV vaccine development.
-
Systems vaccinology: learning to compute the behavior of vaccine induced immunity.Systems vaccinology: learning to compute the behavior of vaccine induced immunity.
-
Systems biology of vaccination in the elderly.Systems biology of vaccination in the elderly.
-
Immunity to viruses: learning from successful human vaccines.Immunity to viruses: learning from successful human vaccines.
-
Systems biological approaches to measure and understand vaccine immunity in humans.Systems biological approaches to measure and understand vaccine immunity in humans.
-
Gene signatures related to B-cell proliferation predict influenza vaccine-induced antibody response.Gene signatures related to B-cell proliferation predict influenza vaccine-induced antibody response.
-
Vaccinology in the era of high-throughput biology.Vaccinology in the era of high-throughput biology.
-
Systems vaccinology: Enabling rational vaccine design with systems biological approaches.Systems vaccinology: Enabling rational vaccine design with systems biological approaches.
-
Systems Vaccinology Applied to DNA Vaccines: Perspective and Challenges.Systems Vaccinology Applied to DNA Vaccines: Perspective and Challenges.
-
Adjuvanting a Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Vaccine with Toll-Like Receptor Ligands Encapsulated in Nanoparticles Induces Persistent Antibody Responses and Enhanced Protection in TRIM5α Restrictive Macaques.Adjuvanting a Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Vaccine with Toll-Like Receptor Ligands Encapsulated in Nanoparticles Induces Persistent Antibody Responses and Enhanced Protection in TRIM5α Restrictive Macaques.
-
Methods for predicting vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity.Methods for predicting vaccine immunogenicity and reactogenicity.
-
Antigenicity prediction and vaccine recommendation of human influenza virus A (H3N2) using convolutional neural networks.Antigenicity prediction and vaccine recommendation of human influenza virus A (H3N2) using convolutional neural networks.
-
Pneumococcal colonization impairs mucosal immune responses to live attenuated influenza vaccine.Pneumococcal colonization impairs mucosal immune responses to live attenuated influenza vaccine.
-
Human Transcriptomic Response to the VSV-Vectored Ebola Vaccine.Human Transcriptomic Response to the VSV-Vectored Ebola Vaccine.
-
Induction of Cell Cycle and NK Cell Responses by Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines against Typhoid Fever.Induction of Cell Cycle and NK Cell Responses by Live-Attenuated Oral Vaccines against Typhoid Fever.
-
Systems Biology Analysis of the Radiation-Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine Reveals a Role for Growth Factors in Protection and Hemostasis Inhibition in Parasite Survival.Systems Biology Analysis of the Radiation-Attenuated Schistosome Vaccine Reveals a Role for Growth Factors in Protection and Hemostasis Inhibition in Parasite Survival.
-
Molecular alterations in human milk in simulated maternal nasal mucosal infection with live attenuated influenza vaccinationMolecular alterations in human milk in simulated maternal nasal mucosal infection with live attenuated influenza vaccination
-
Systems biology of immunity to MF59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines in early childhood.Systems biology of immunity to MF59-adjuvanted versus nonadjuvanted trivalent seasonal influenza vaccines in early childhood.
-
Systems analysis of protective immune responses to RTS,S malaria vaccination in humans.Systems analysis of protective immune responses to RTS,S malaria vaccination in humans.
-
Systems vaccinology.Systems vaccinology.
-
Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans.Systems biology approach predicts immunogenicity of the yellow fever vaccine in humans.
-
Systems biology of vaccination for seasonal influenza in humans.Systems biology of vaccination for seasonal influenza in humans.
-
Prior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in childrenPrior upregulation of interferon pathways in the nasopharynx impacts viral shedding following live attenuated influenza vaccine challenge in children
-
Systems Analysis of Immunity to Influenza Vaccination across Multiple Years and in Diverse Populations Reveals Shared Molecular Signatures.Systems Analysis of Immunity to Influenza Vaccination across Multiple Years and in Diverse Populations Reveals Shared Molecular Signatures.
-
Molecular signatures of antibody responses derived from a systems biology study of five human vaccines.Molecular signatures of antibody responses derived from a systems biology study of five human vaccines.
-
Long noncoding RNAs are involved in multiple immunological pathways in response to vaccination.Long noncoding RNAs are involved in multiple immunological pathways in response to vaccination.
-
Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans.Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans.
-
Hidden in plain sight: uncovering the role of CREB1 in HIV-1 vaccine-induced immunityHidden in plain sight: uncovering the role of CREB1 in HIV-1 vaccine-induced immunity
-
Transcriptomic signatures induced by the Ebola virus vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV-GP in adult cohorts in Europe, Africa, and North America: a molecular biomarker studyTranscriptomic signatures induced by the Ebola virus vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV-GP in adult cohorts in Europe, Africa, and North America: a molecular biomarker study
-
Baseline gene signatures of reactogenicity to Ebola vaccination: a machine learning approach across multiple cohortsBaseline gene signatures of reactogenicity to Ebola vaccination: a machine learning approach across multiple cohorts
-
Global blood miRNA profiling unravels early signatures of immunogenicity of Ebola vaccine rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GPGlobal blood miRNA profiling unravels early signatures of immunogenicity of Ebola vaccine rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP
-
COVID-19 vaccination atlas using an integrative systems vaccinology approach.COVID-19 vaccination atlas using an integrative systems vaccinology approach.
-
Emulsion adjuvant-induced uric acid release modulates optimal immunogenicity by targeting dendritic cells and B cells.Emulsion adjuvant-induced uric acid release modulates optimal immunogenicity by targeting dendritic cells and B cells.
-
System vaccinology analysis of predictors and mechanisms of antibody response durability to multiple vaccines in humans.System vaccinology analysis of predictors and mechanisms of antibody response durability to multiple vaccines in humans.
-
Poly I:C elicits broader and stronger humoral and cellular responses to a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein malaria vaccine than Alhydrogel in mice.Poly I:C elicits broader and stronger humoral and cellular responses to a Plasmodium vivax circumsporozoite protein malaria vaccine than Alhydrogel in mice.