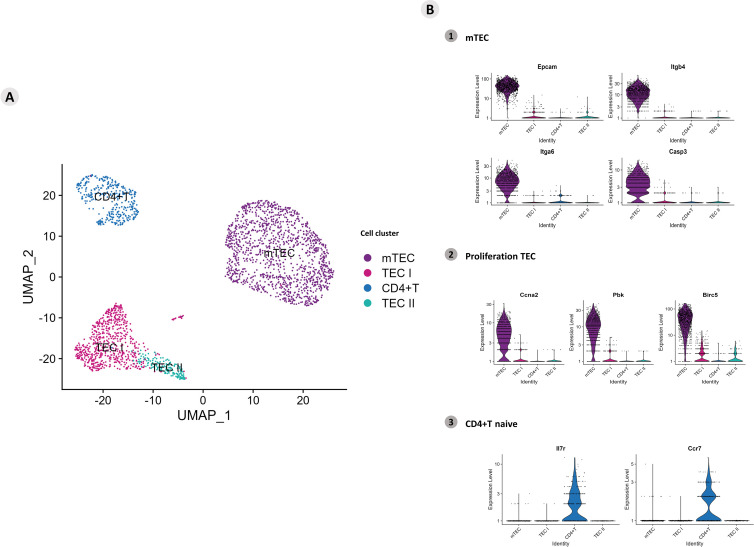
The single-cell transcriptome of mTECs and CD4(+) thymocytes under adhesion revealed heterogeneity of mTECs and a network controlled by Aire and lncRNAs.
To further understand the impact of deficiency of the autoimmune regulator (Aire) gene during the adhesion of medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTECs) to thymocytes, we sequenced single-cell libraries (scRNA-seq) obtained from Aire wild-type (WT) (Airewt/wt ) or Aire-deficient (Airewt/mut ) mTECs cocultured with WT single-positive (SP) CD4+ thymocytes. Although the libraries differed in their mRNA and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) profiles, indicating that mTECs were heterogeneous in terms of their transcriptome, UMAP clustering revealed that both mTEC lines expressed their specific markers, i.e., Epcam, Itgb4, Itga6, and Casp3 in resting mTECs and Ccna2, Pbk, and Birc5 in proliferative mTECs. Both cocultured SP CD4+ thymocytes remained in a homogeneous cluster expressing the Il7r and Ccr7 markers. Comparisons of the two types of cocultures revealed the differential expression of mRNAs that encode transcription factors (Zfpm2,Satb1, and Lef1), cell adhesion genes (Itgb1) in mTECs, and Themis in thymocytes, which is associated with the regulation of positive and negative selection. At the single-cell sequencing resolution, we observed that Aire acts on both Aire WT and Aire-deficient mTECs as an upstream controller of mRNAs, which encode transcription factors or adhesion proteins that, in turn, are posttranscriptionally controlled by lncRNAs, for example, Neat1, Malat1, Pvt1, and Dancr among others. Under Aire deficiency, mTECs dysregulate the expression of MHC-II, CD80, and CD326 (EPCAM) protein markers as well as metabolism and cell cycle-related mRNAs, which delay the cell cycle progression. Moreover, when adhered to mTECs, WT SP CD4+ or CD8+ thymocytes modulate the expression of cell activation proteins, including CD28 and CD152/CTLA4, and the expression of cellular metabolism mRNAs. These findings indicate a complex mechanism through which an imbalance in Aire expression can affect mTECs and thymocytes during adhesion.
Authors
Monteiro CJ, Duarte MJ, Machado MCV, Mascarenhas RS
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Systems Immunology of Human Diseases
Lista de serviços
-
As antisense RNA gets intronic.As antisense RNA gets intronic.
-
Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.Androgen responsive intronic non-coding RNAs.
-
Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.Conserved tissue expression signatures of intronic noncoding RNAs transcribed from human and mouse loci.
-
The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation.
-
Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer.
-
Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.Insight Into the Long Noncoding RNA and mRNA Coexpression Profile in the Human Blood Transcriptome Upon Leishmania infantum Infection.
-
Long non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunityLong non-coding RNAs associated with infection and vaccine-induced immunity
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophagesComparative transcriptomic analysis of long noncoding RNAs in Leishmania-infected human macrophages
-
SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.