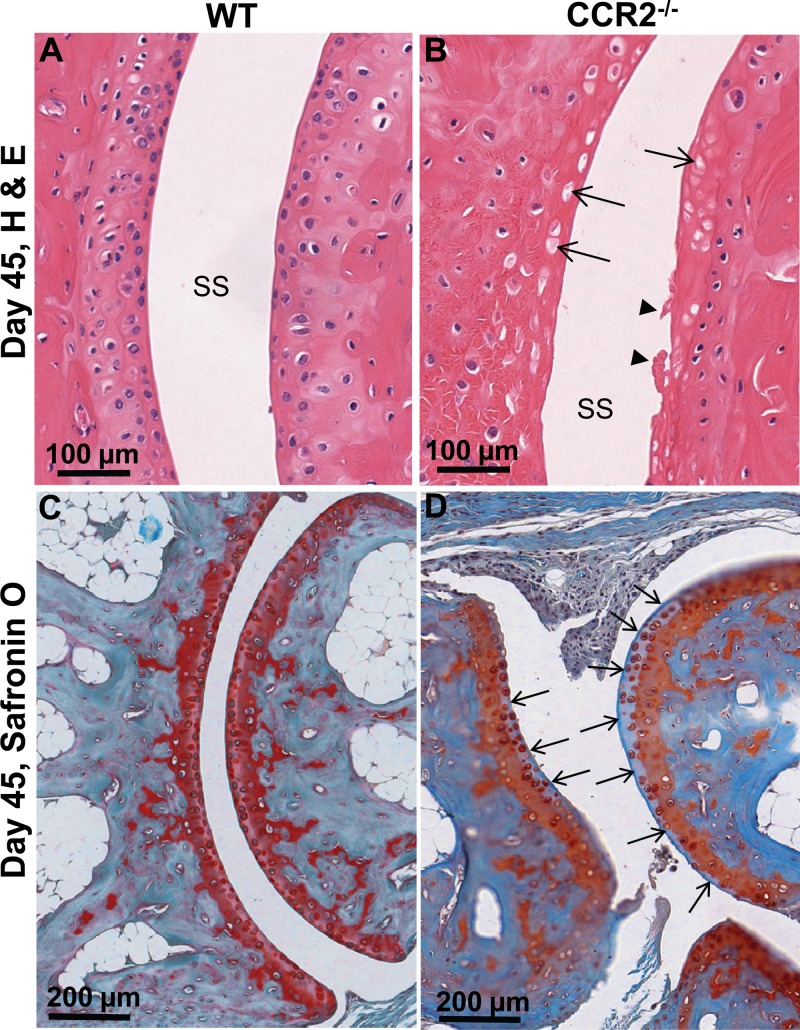
CCR2 deficiency promotes exacerbated chronic erosive neutrophil-dominated chikungunya virus arthritis.
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a member of a globally distributed group of arthritogenic alphaviruses that cause weeks to months of debilitating polyarthritis/arthralgia, which is often poorly managed with current treatments. Arthritic disease is usually characterized by high levels of the chemokine CCL2 and a prodigious monocyte/macrophage infiltrate. Several inhibitors of CCL2 and its receptor CCR2 are in development and may find application for treatment of certain inflammatory conditions, including autoimmune and viral arthritides. Here we used CCR2(-/-) mice to determine the effect of CCR2 deficiency on CHIKV infection and arthritis. Although there were no significant changes in viral load or RNA persistence and only marginal changes in antiviral immunity, arthritic disease was substantially increased and prolonged in CCR2(-/-) mice compared to wild-type mice. The monocyte/macrophage infiltrate was replaced in CCR2(-/-) mice by a severe neutrophil (followed by an eosinophil) infiltrate and was associated with changes in the expression levels of multiple inflammatory mediators (including CXCL1, CXCL2, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor [G-CSF], interleukin-1β [IL-1β], and IL-10). The loss of anti-inflammatory macrophages and their activities (e.g., efferocytosis) was also implicated in exacerbated inflammation. Clear evidence of cartilage damage was also seen in CHIKV-infected CCR2(-/-) mice, a feature not normally associated with alphaviral arthritides. Although recruitment of CCR2(+) monocytes/macrophages can contribute to inflammation, it also appears to be critical for preventing excessive pathology and resolving inflammation following alphavirus infection. Caution might thus be warranted when considering therapeutic targeting of CCR2/CCL2 for the treatment of alphaviral arthritides. Here we describe the first analysis of viral arthritis in mice deficient for the chemokine receptor CCR2. CCR2 is thought to be central to the monocyte/macrophage-dominated inflammatory arthritic infiltrates seen after infection with arthritogenic alphaviruses such as chikungunya virus. Surprisingly, the viral arthritis caused by chikungunya virus in CCR2-deficient mice was more severe, prolonged, and erosive and was neutrophil dominated, with viral replication and persistence not being significantly affected. Monocytes/macrophages recruited by CCL2 thus also appear to be important for both preventing even worse pathology mediated by neutrophils and promoting resolution of inflammation. Caution might thus be warranted when considering the use of therapeutic agents that target CCR2/CCL2 or inflammatory monocytes/macrophages for the treatment of alphaviral (and perhaps other viral) arthritides. Individuals with diminished CCR2 responses (due to drug treatment or other reasons) may also be at risk of exacerbated arthritic disease following alphaviral infection.
Authors
Yee Suan Poo; Helder Nakaya; Joy Gardner; Thibaut Larcher; Wayne A Schroder; Thuy T Le; Lee D Major; Andreas Suhrbier
External link
Publication Year
Publication Journal
Associeted Project
Microbiology or Immunology
Lista de serviços
-
Phenotype, function, and gene expression profiles of programmed death-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy human adults.Phenotype, function, and gene expression profiles of programmed death-1(hi) CD8 T cells in healthy human adults.
-
Repression of bacterial lipoprotein production by Francisella novicida facilitates evasion of innate immune recognition.Repression of bacterial lipoprotein production by Francisella novicida facilitates evasion of innate immune recognition.
-
CCR2 deficiency promotes exacerbated chronic erosive neutrophil-dominated chikungunya virus arthritis.CCR2 deficiency promotes exacerbated chronic erosive neutrophil-dominated chikungunya virus arthritis.
-
Multiple immune factors are involved in controlling acute and chronic chikungunya virus infection.Multiple immune factors are involved in controlling acute and chronic chikungunya virus infection.
-
Myeloperoxidase in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: Production and subcellular localization.Myeloperoxidase in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: Production and subcellular localization.
-
Analysis of LexA binding sites and transcriptomics in response to genotoxic stress in Leptospira interrogans.Analysis of LexA binding sites and transcriptomics in response to genotoxic stress in Leptospira interrogans.
-
SerpinB2 Deficiency Results in a Stratum Corneum Defect and Increased Sensitivity to Topically Applied Inflammatory Agents.SerpinB2 Deficiency Results in a Stratum Corneum Defect and Increased Sensitivity to Topically Applied Inflammatory Agents.
-
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase 2 regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell regeneration.Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase 2 regulates hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell regeneration.
-
N-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Blockade Prevents Neuronal Death Induced by Zika Virus InfectionN-Methyl-d-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor Blockade Prevents Neuronal Death Induced by Zika Virus Infection
-
Blood Gene Signatures of Chagas Cardiomyopathy With or Without Ventricular Dysfunction.Blood Gene Signatures of Chagas Cardiomyopathy With or Without Ventricular Dysfunction.
-
In situ Immune Signatures and Microbial Load at the Nasopharyngeal Interface in Children With Acute Respiratory InfectionIn situ Immune Signatures and Microbial Load at the Nasopharyngeal Interface in Children With Acute Respiratory Infection
-
TGF-β signalling defect is linked to low CD39 expression on regulatory T cells and methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis.TGF-β signalling defect is linked to low CD39 expression on regulatory T cells and methotrexate resistance in rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Genetic sequence characterization and naturally acquired immune response to Plasmodium vivax Rhoptry Neck Protein 2 (PvRON2).Genetic sequence characterization and naturally acquired immune response to Plasmodium vivax Rhoptry Neck Protein 2 (PvRON2).
-
Molecular degree of perturbation of plasma inflammatory markers associated with tuberculosis reveals distinct disease profiles between Indian and Chinese populations.Molecular degree of perturbation of plasma inflammatory markers associated with tuberculosis reveals distinct disease profiles between Indian and Chinese populations.
-
SerpinB2 inhibits migration and promotes a resolution phase signature in large peritoneal macrophages.SerpinB2 inhibits migration and promotes a resolution phase signature in large peritoneal macrophages.
-
Biological sex influences antibody responses to routine vaccinations in the first year of life.Biological sex influences antibody responses to routine vaccinations in the first year of life.
-
Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation.Gasdermin D inhibition prevents multiple organ dysfunction during sepsis by blocking NET formation.
-
Susceptibility of the Elderly to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: ACE-2 Overexpression, Shedding, and Antibody-dependent Enhancement (ADE).Susceptibility of the Elderly to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: ACE-2 Overexpression, Shedding, and Antibody-dependent Enhancement (ADE).
-
Variants in the Kisspeptin-GnRH Pathway Modulate the Hormonal Profile and Reproductive Outcomes.Variants in the Kisspeptin-GnRH Pathway Modulate the Hormonal Profile and Reproductive Outcomes.
-
Hydroquinone exposure alters the morphology of lymphoid organs in vaccinated C57Bl/6 mice.Hydroquinone exposure alters the morphology of lymphoid organs in vaccinated C57Bl/6 mice.
-
P2x7 Receptor Signaling Blockade Reduces Lung Inflammation and Necrosis During Severe Experimental Tuberculosis.P2x7 Receptor Signaling Blockade Reduces Lung Inflammation and Necrosis During Severe Experimental Tuberculosis.
-
Neuroinflammation at single cell level: What is new?Neuroinflammation at single cell level: What is new?
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing of Leishmania infantum chagasi Isolates from Honduras and BrazilWhole-Genome Sequencing of Leishmania infantum chagasi Isolates from Honduras and Brazil
-
Pediatric COVID-19 patients in South Brazil show abundant viral mRNA and strong specific anti-viral responsesPediatric COVID-19 patients in South Brazil show abundant viral mRNA and strong specific anti-viral responses
-
Rapid dose-dependent Natural Killer (NK) cell modulation and cytokine responses following human rVSV-ZEBOV Ebolavirus vaccination.Rapid dose-dependent Natural Killer (NK) cell modulation and cytokine responses following human rVSV-ZEBOV Ebolavirus vaccination.
-
An Experimental DUAL Model of Advanced Liver DamageAn Experimental DUAL Model of Advanced Liver Damage
-
Colorimetric RT-LAMP SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic sensitivity relies on color interpretation and viral loadColorimetric RT-LAMP SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic sensitivity relies on color interpretation and viral load
-
Distinct TLR adjuvants differentially stimulate systemic and local innate immune responses in nonhuman primates.Distinct TLR adjuvants differentially stimulate systemic and local innate immune responses in nonhuman primates.
-
Lower temperatures reduce type I interferon activity and promote alphaviral arthritis.Lower temperatures reduce type I interferon activity and promote alphaviral arthritis.
-
Acute Zika Virus Infection in an Endemic Area Shows Modest Proinflammatory Systemic Immunoactivation and Cytokine-Symptom Associations.Acute Zika Virus Infection in an Endemic Area Shows Modest Proinflammatory Systemic Immunoactivation and Cytokine-Symptom Associations.
-
Dengue virus infection induces expansion of a CD14(+)CD16(+) monocyte population that stimulates plasmablast differentiation.Dengue virus infection induces expansion of a CD14(+)CD16(+) monocyte population that stimulates plasmablast differentiation.
-
Uptake of Plasmodium chabaudi hemozoin drives Kupffer cell death and fuels superinfectionsUptake of Plasmodium chabaudi hemozoin drives Kupffer cell death and fuels superinfections
-
Platelet-monocyte interaction amplifies thromboinflammation through tissue factor signaling in COVID-19Platelet-monocyte interaction amplifies thromboinflammation through tissue factor signaling in COVID-19
-
Flavivirus-Mediating B Cell Differentiation Into Antibody-Secreting Cells in Humans Is Associated With the Activation of the Tryptophan Metabolism.Flavivirus-Mediating B Cell Differentiation Into Antibody-Secreting Cells in Humans Is Associated With the Activation of the Tryptophan Metabolism.
-
Acute Inflammation Is a Predisposing Factor for Weight Gain and Insulin ResistanceAcute Inflammation Is a Predisposing Factor for Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance
-
Initial viral load determines the magnitude of the human CD8 T cell response to yellow fever vaccination.Initial viral load determines the magnitude of the human CD8 T cell response to yellow fever vaccination.
-
SARS-CoV-2 infected children form early immune memory responses dominated by nucleocapsid-specific CD8+ T cells and antibodiesSARS-CoV-2 infected children form early immune memory responses dominated by nucleocapsid-specific CD8+ T cells and antibodies
-
Differentiation of Memory CD8 T Cells Unravel Gene Expression Pattern Common to Effector and Memory PrecursorsDifferentiation of Memory CD8 T Cells Unravel Gene Expression Pattern Common to Effector and Memory Precursors
-
Crucial role for T cell-intrinsic IL-18R-MyD88 signaling in cognate immune response to intracellular parasite infection.Crucial role for T cell-intrinsic IL-18R-MyD88 signaling in cognate immune response to intracellular parasite infection.
-
Canonical PI3Kγ signaling in myeloid cells restricts Trypanosoma cruzi infection and dampens chagasic myocarditis.Canonical PI3Kγ signaling in myeloid cells restricts Trypanosoma cruzi infection and dampens chagasic myocarditis.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation contributes to high fat diet induced vascular dysfunctionAryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation contributes to high fat diet induced vascular dysfunction
-
Tissue-resident glial cells associate with tumoral vasculature and promote cancer progressionTissue-resident glial cells associate with tumoral vasculature and promote cancer progression
-
MS-Driven Metabolic Alterations Are Recapitulated in iPSC-Derived AstrocytesMS-Driven Metabolic Alterations Are Recapitulated in iPSC-Derived Astrocytes
-
Determinants of antibody persistence across doses and continents after single-dose rVSV-ZEBOV vaccination for Ebola virus disease: an observational cohort study.Determinants of antibody persistence across doses and continents after single-dose rVSV-ZEBOV vaccination for Ebola virus disease: an observational cohort study.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition enhances chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain by suppressing neuroimmune antinociceptive signalingPD-1/PD-L1 inhibition enhances chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain by suppressing neuroimmune antinociceptive signaling
-
Knockout of cellular prion protein in glioblastoma affects the expression of Wnt signaling genesKnockout of cellular prion protein in glioblastoma affects the expression of Wnt signaling genes
-
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade abrogates a dysfunctional innate-adaptive immune axis in critical beta-coronavirus diseasePD-1/PD-L1 blockade abrogates a dysfunctional innate-adaptive immune axis in critical beta-coronavirus disease
-
The T helper type 2 response to cysteine proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS-mediated signaling.The T helper type 2 response to cysteine proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS-mediated signaling.
-
Chronic but not acute virus infection induces sustained expansion of myeloid suppressor cell numbers that inhibit viral-specific T cell immunity.Chronic but not acute virus infection induces sustained expansion of myeloid suppressor cell numbers that inhibit viral-specific T cell immunity.
-
TLR5-mediated sensing of gut microbiota is necessary for antibody responses to seasonal influenza vaccination.TLR5-mediated sensing of gut microbiota is necessary for antibody responses to seasonal influenza vaccination.
-
Activation of beta-catenin in dendritic cells regulates immunity versus tolerance in the intestine.Activation of beta-catenin in dendritic cells regulates immunity versus tolerance in the intestine.
-
Programming the magnitude and persistence of antibody responses with innate immunity.Programming the magnitude and persistence of antibody responses with innate immunity.
-
Specific inhibition of NLRP3 in chikungunya disease reveals a role for inflammasomes in alphavirus-induced inflammation.Specific inhibition of NLRP3 in chikungunya disease reveals a role for inflammasomes in alphavirus-induced inflammation.
-
Defining antigen-specific plasmablast and memory B cell subsets in human blood after viral infection or vaccination.Defining antigen-specific plasmablast and memory B cell subsets in human blood after viral infection or vaccination.
-
Vaccine activation of the nutrient sensor GCN2 in dendritic cells enhances antigen presentation.Vaccine activation of the nutrient sensor GCN2 in dendritic cells enhances antigen presentation.
-
The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation.The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation.
-
Defining CD8+ T cells that provide the proliferative burst after PD-1 therapy.Defining CD8+ T cells that provide the proliferative burst after PD-1 therapy.
-
Sepsis expands a CD39(+) plasmablast population that promotes immunosuppression via adenosine-mediated inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activitySepsis expands a CD39(+) plasmablast population that promotes immunosuppression via adenosine-mediated inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activity
-
Antibody responses to recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-Zaire Ebolavirus vaccination for Ebola virus disease across doses and continents: 5-year durabilityAntibody responses to recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-Zaire Ebolavirus vaccination for Ebola virus disease across doses and continents: 5-year durability
-
Combining IP(3) affinity chromatography and bioinformatics reveals a novel protein-IP(3) binding site on Plasmodium falciparum MDR1 transporter.Combining IP(3) affinity chromatography and bioinformatics reveals a novel protein-IP(3) binding site on Plasmodium falciparum MDR1 transporter.
-
SARS-CoV-2 uses CD4 to infect T helper lymphocytesSARS-CoV-2 uses CD4 to infect T helper lymphocytes
-
Expression of HMGCS2 in intestinal epithelial cells is downregulated in inflammatory bowel disease associated with endoplasmic reticulum stressExpression of HMGCS2 in intestinal epithelial cells is downregulated in inflammatory bowel disease associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress
-
Immunodominant antibody responses directed to SARS-CoV-2 hotspot mutation sites and risk of immune escapeImmunodominant antibody responses directed to SARS-CoV-2 hotspot mutation sites and risk of immune escape
-
Novel therapeutic avenues for the study of chronic liver disease and regeneration: The foundation of the Iberoamerican Consortium for the study of liver CirrhosisNovel therapeutic avenues for the study of chronic liver disease and regeneration: The foundation of the Iberoamerican Consortium for the study of liver Cirrhosis
-
Identification of pathogenic variants in the Brazilian cohort with Familial hypercholesterolemia using exon-targeted gene sequencingIdentification of pathogenic variants in the Brazilian cohort with Familial hypercholesterolemia using exon-targeted gene sequencing
-
CASP4/11 Contributes to NLRP3 Activation and COVID-19 ExacerbationCASP4/11 Contributes to NLRP3 Activation and COVID-19 Exacerbation
-
S100A9 Drives the Chronification of Psoriasiform Inflammation by Inducing IL-23/Type 3 ImmunityS100A9 Drives the Chronification of Psoriasiform Inflammation by Inducing IL-23/Type 3 Immunity
-
Clinical markers of post-Chikungunya chronic inflammatory joint disease: A Brazilian cohortClinical markers of post-Chikungunya chronic inflammatory joint disease: A Brazilian cohort
-
Replication, safety and immunogenicity of the vectored Ebola vaccine rVSV-ΔG-ZEBOV-GP in a sub-Saharan African paediatric population: A randomised controlled, open-label trial in children aged 1-12 years living in Lambaréné, Gabon.Replication, safety and immunogenicity of the vectored Ebola vaccine rVSV-ΔG-ZEBOV-GP in a sub-Saharan African paediatric population: A randomised controlled, open-label trial in children aged 1-12 years living in Lambaréné, Gabon.
-
Phenotypical characterization of exteroceptive sensation and pain symptoms on diabetic patients.Phenotypical characterization of exteroceptive sensation and pain symptoms on diabetic patients.